CRaC is an OpenJDK project that defines a new Java API. Use the CRaC API to coordinate resources during checkpoint and restore operations.
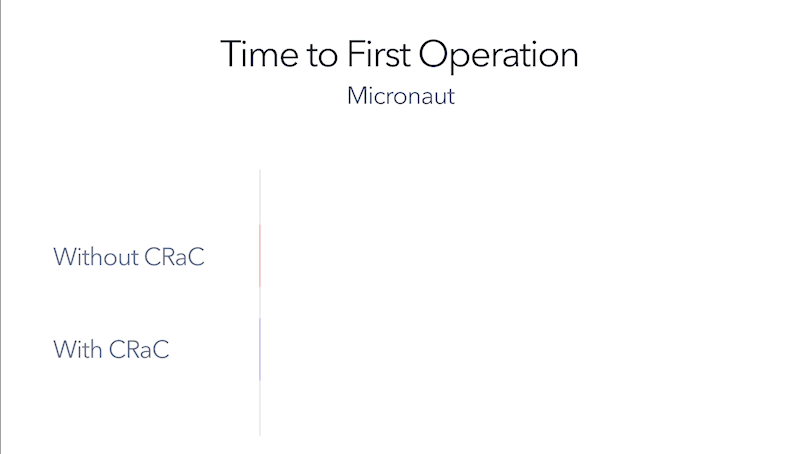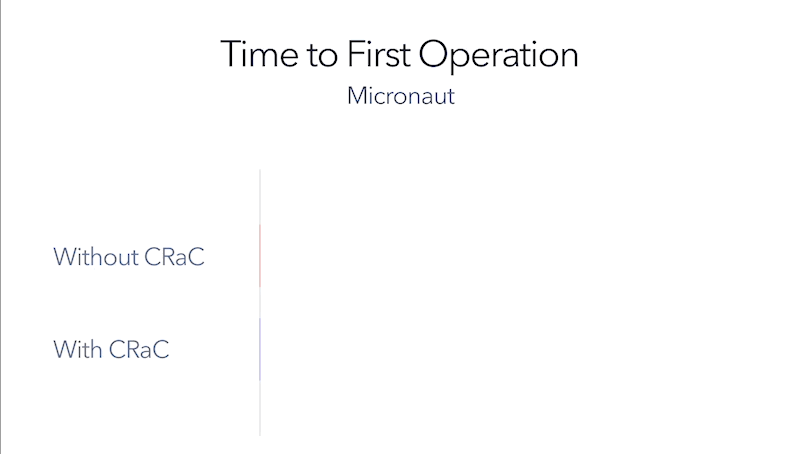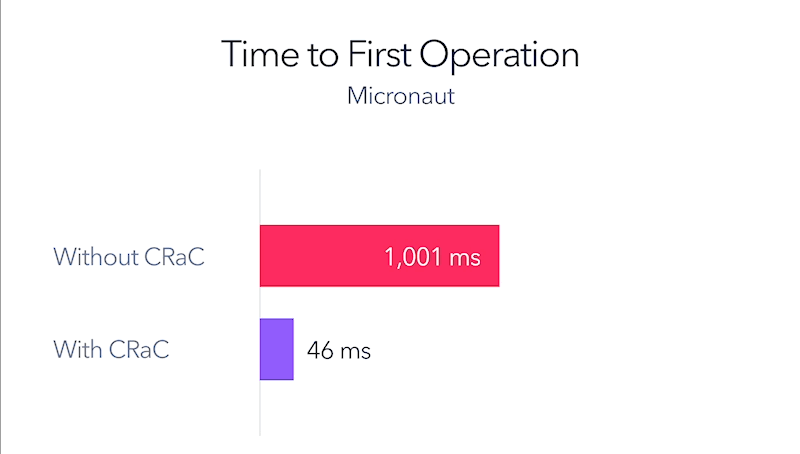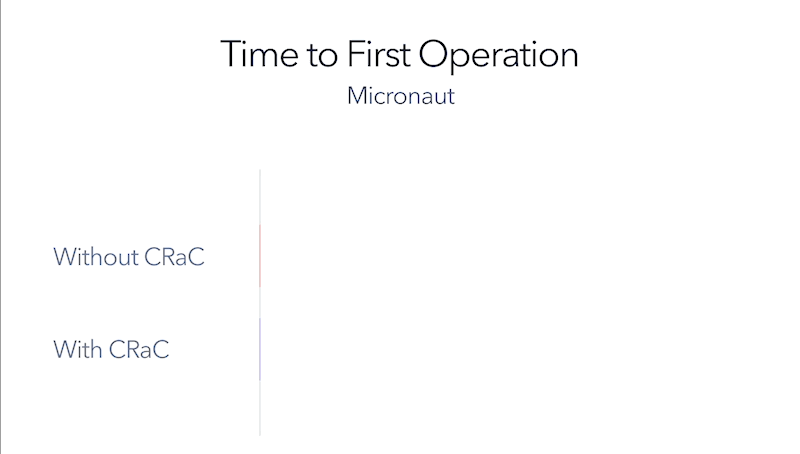
“CRaC has generated immense interest among the Java developer community and provides a compelling, resource-efficient approach for improving startup and warmup times.”
— Sergio del Amo, Micronaut Product Development Lead
“Project CRaC’s checkpoint restore approach is very promising for the immediate startup of Spring applications on the JVM. Our collaboration with Azul delivered some great initial results already.”
— Juergen Hoeller, project lead and co-founder of the Spring Framework project
Azul initiated the OpenJDK CRaC project because we know how important it will be for the entire ecosystem for Java applications to start instantaneously and at full speed. Developers from open-source projects like Micronaut and Quarkus have added support for CRaC, and Azul released JDK 17 Linux x84 64-bit with CRaC support as part of the April 2023 quarterly update. Developers can now deploy applications using CRaC in production with confidence that the JDK will be continuously updated.
First GitHub commit
OpenJDK project is proposed
OpenJDK accepts the project
Initial CRaC support added to Quarkus
CRaC working in AWS Lambda
Micronaut releases CRaC 1.0.0
CRaC is first available in supported and unsupported JDK builds —specifically in JDK 17 Linux x86 64-bit from Azul
CRaC is an acronym. It stands for Coordinated Restore at Checkpoint. The CRaC Java API allows for the coordination of resources during checkpoint and restore operations.
CRaC Java API helps to coordinate JDK and application resources with the checkpoint/restore mechanism.
It allows you to close files and connections, dump cache before checkpoint and reopen/recover everything when the application is restored from the image.
You can get started by downloading Azul Zulu builds of OpenJDK with CRaC support and reading the CRaC documentation. This is a build created by Azul and released as a free-to-use community edition of Azul Zulu Builds of OpenJDK. The build is generally available build and will continue to be updated by Azul. Commercial support is also available with Azul Platform Core.
CRaC is an open-source project under OpenJDK. Like OpenJDK, CRaC is free to use.
A great place to get answers for CRaC questions is to join the Foojay.io community. If you are an Azul customer, you can also connect with a support engineer.
Yes, you can. See the CRaC documentation for more details.
The size of the checkpoint files depends on the size of the heap that you use in your setup. You can think about the checkpoint like a heapdump. Bigger heap means bigger files.
Yes, that is possible because everything is bound to the Linux session using its PID (Process ID), which also includes off-heap memory.
Currently, Azul Zulu Builds of OpenJDK with CRaC support are available only on Linux. We are considering future implementations.
You can develop your applications and libraries for CRaC on any operating system using the library available at Sonatype. With this you can use your Windows machine to write the CRaC code and deploy it to your Linux machine where it will then make use of CRaC.
Graphical WS/Swing/Java FX applications are not yet supported with CRaC. Support for graphics is coming in the next releases.
The principal use case is to reduce the startup and warmup times of the Java applications that have to be restarted frequently or that experience long startup and warmup times.
Superfast JVM Startup by Gerrit Grunwald